In recent years, generative AI has moved from a niche research topic to a popular technology shaping how we write, design, code, and create. Generative AI is emerging as a phenomenon in the industries and is used to create rather than analyze, be it an email drafting chatbot or a system to generate pictures, tunes, and even code.
- What Is Generative AI?
- How Generative AI Works
- Key Generative AI Models Explained
- Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Image Generation Models
- Audio and Video Generation Models
- Multimodal Models
- Generative AI vs Traditional AI
- Common Examples of Generative AI
- Real-World Applications of Generative AI
- Software Development
- Design and Creative Industries
- Healthcare and Research
- Education and Training
- Business Automation
- Why Generative AI Is So Powerful
- Limitations and Challenges of Generative AI
- Hallucinations and Accuracy Issues
- Bias in Training Data
- Ethical and Copyright Challenges
- Over-Reliance Risks
- Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
- Generative AI in Business and Everyday Life
- Future of Generative AI
AI is, in its essence, an artificial intelligence system capable of producing new content using the patterns that have been learned from existing data. Innovative AI systems, in contrast to the standard ones, are targeted toward generating original results, including text, images, audio, video, and artificially generated data.
This article explains what generative AI is and how it works in simple, clear terms. It is written in an easy-to-understand manner for beginners, professionals, marketers, students, and decision-makers, but does not require extensive technical expertise. By the end, you’ll understand how AI works, where it’s used, why it’s powerful, and where its limits lie.
What Is Generative AI?
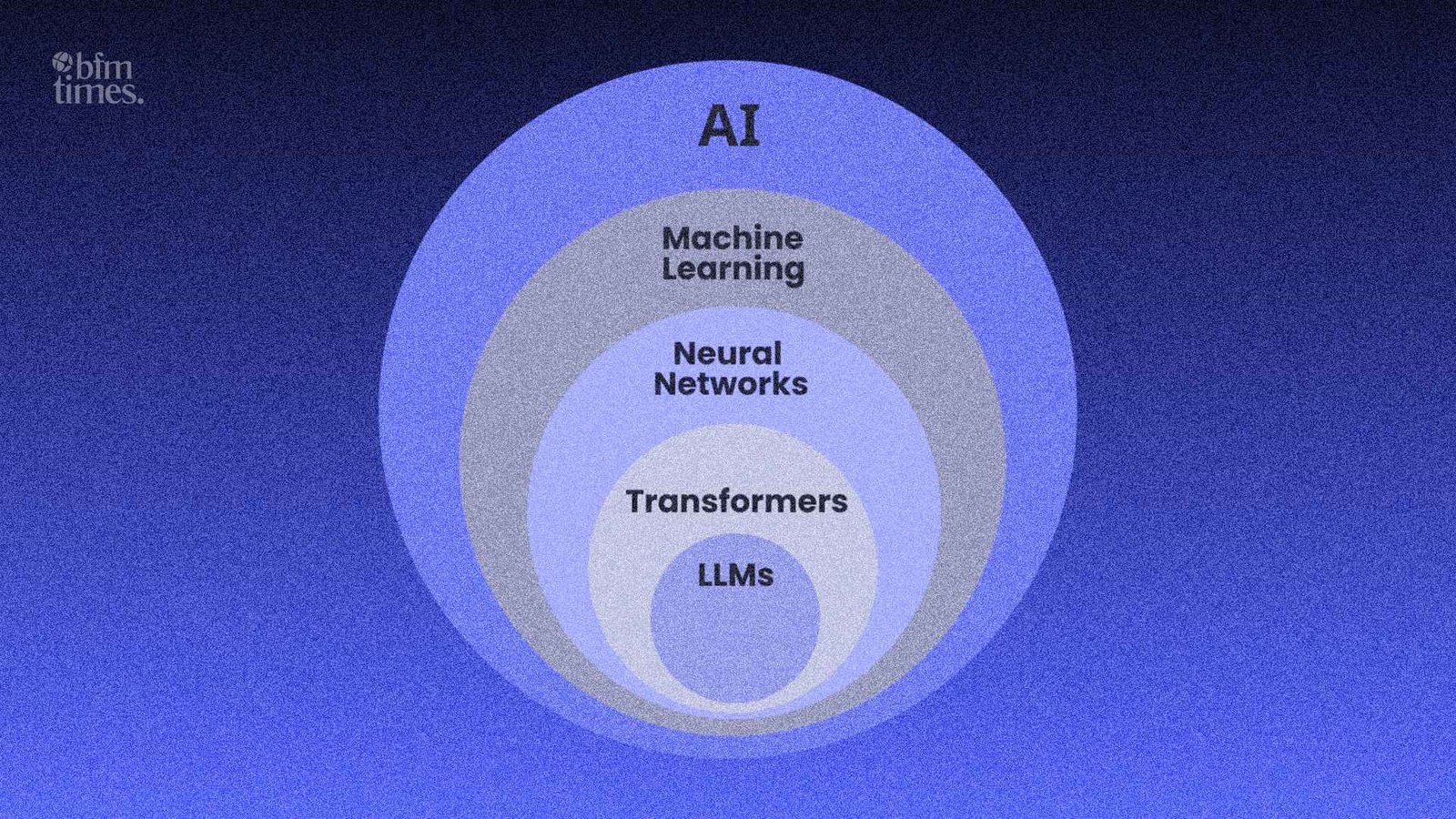
Generative AI is a subdivision of artificial intelligence that involves the production of new information as opposed to the analysis or classification of existing information. These systems identify patterns, structures, and relationships among large datasets, build a body of knowledge on these datasets, and generate content that is similar to that created by humans.
In simple terms, generative artificial intelligence answers questions like:
- Can a machine write a paragraph?
- Can it design an image from a description?
- Can it generate music, code, or video?
The reply to this is yes, but under certain limitations.
How Generative AI Differs from Traditional AI
The traditional AI systems are usually developed to:
- Detect spam emails
- Recognize faces
- Forecast the future using previous information.
- Classify images or text
Generative AI, conversely:
- Generates new text, pictures, sound, or information.
- Writes imaginatively but not necessarily critically.
- Reacts to stimuli and not rigid regulations.
The core purpose of generative artificial intelligence is generation, something new that has never been created previously, according to learned patterns.
How Generative AI Works
Generative artificial intelligence does not need advanced mathematics to understand the working mechanism. On a higher level, the process can be divided into three basic steps.
1. Training on Large Datasets
Generative artificial intelligence models use datasets containing massive amounts of data that might contain:
- Books, articles, and texts on the internet.
- Images with descriptions
- Audio recordings and transcripts.
- Code repositories
- The structured data and the unstructured data.
The system is not learning word-for-word during training. Rather, it picks up statistical habits, how words are connected, how shapes are composed of objects, or how series proceed through time.
2. Learning Patterns and Probabilities
Once trained, generative AI models understand:
- Structural and grammatical aspects of language.
- Patterns in the visuals, such as edges, colors, and textures.
- Interrelations among concepts.
- Likelihood of the succession.
For example, in text generation, the model is used to predict the most probable next word given some context. In image generation, it forecasts pixel patterns that are consistent with a prompt.
3. Generating Outputs
At the prompt of a user, the model:
- Interprets the input
- Applies learned patterns
- Generates an output step by step
This is the core of how generative AI works in the form of predicting and building the content using the likelihood instead of strict regulations.
An example that applies: generative AI is the next stage of an autocomplete system that understands meaning, not just words.
Key Generative AI Models Explained
Various categories of AI models are used as generative artificial intelligence to produce various types of content. The key categories are discussed below with an actual example.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
A Large Language Model Generative AI systems are trained on huge quantities of text. They produce language responses that are similar to human beings and are commonly applied in chatbots, content drafting, summarization, and translation.
Common uses include:
- Writing articles or emails
- Answering questions
- Summarizing documents
- Generating dialogue
One of the most visible generative AI models nowadays is LLDMs.
Image Generation Models
These AI generative models generate images due to text description or reference input. They are capable of seeing visual patterns, styles, and relationships of objects.
Examples include:
- Creating marketing visuals
- Designing concept art
- Generating illustrations
- Enhancing photos
One of the most common examples of generative artificial intelligence in the field of creativity is image generation.
Audio and Video Generation Models
Generative AI models that are audio-centered are capable of:
- Generate speech
- Clone voices (with restrictions)
- Produce music or sound effects.
Video generation models work on:
- Animated content
- Short video clips
- Visual storytelling
These models have been utilized in the media, entertainment, and education.
Multimodal Models
Multimodal generative artificial intelligence systems have the ability to process several input modalities at once: text, images, and audio.
For example:
- An image analyzing system that then explains itself in text.
- A script and image-generating video system.
The next phase of generative AI models is multi-modal systems that are based on a combination of various types of understanding.
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
The distinction between generative AI and conventional AI can be used to explain the distinct value of the former.
| Aspect | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
| Approach | Rule-based or predictive | Learning-based and creative |
| Output | Decisions or classifications | New content |
| Focus | Automation and analysis | Generation and synthesis |
| Flexibility | Limited to defined tasks | Adaptable across tasks |
Traditional AI provides answers to what is, whereas generative artificial intelligence provides answers to what could be.
Common Examples of Generative AI
In order to further comprehend its scope, the following are typical examples of generative AI in industries.
Text Generation
- Chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Blog posts and writing documents.
- Email responses
- Product descriptions
Marketers and businesses are common users of text-based generative AI applications.
Image Generation
- Marketing creatives
- Social media visuals
- Branding concepts
- Product mockups
Video and Audio
- Voice narration
- Short-form videos
- Music generation
- Training content
Code Generation
- Writing code snippets
- Describing programming reasoning.
- Debugging assistance
- Documentation creation
Data Simulation
- Test data that is synthetic.
- Machine learning system training.
- Scenario modeling
These generative artificial intelligence examples can show that it is not confined to chat interfaces.
Real-World Applications of Generative AI
Marketing and Content Creation.
Generative artificial intelligence assists marketers in:
- Draft content faster
- Generate ideas
- Repurpose materials
- Create visuals at scale
Many generative artificial intelligence applications do not substitute human creativity since they assist in content workflows.
Software Development
Generative artificial intelligence is applied by developers in:
- Code suggestions
- Documentation
- Testing scenarios
- Learning new frameworks
Design and Creative Industries
Generative artificial intelligence is used by designers to:
- Explore concepts
- Create variations
- Speed up ideation
Healthcare and Research
Generative artificial intelligence can be used in healthcare to:
- Medical imaging analysis
- Drug discovery simulations
- Research summarization
Education and Training
Generative AI enables:
- Individualized learning resources.
- Practice questions
- Simplified explanations
Business Automation
Generative AI is used by businesses to:
- Draft reports
- Create customer reactions.
- Enhance internal productivity.
These applications of generative artificial intelligence demonstrate how the technology aids and does not replace human labor.
Why Generative AI Is So Powerful
There are a number of fundamental strengths behind the increasing usage of generative AI.
Speed and Scalability
AI can create content in seconds and assist teams to scale production without incurring proportional cost changes or time.
Creativity Assistance
Instead of substituting creativity, AI enhances creativity by providing:
- Drafts
- Variations
- New perspectives
Cost Efficiency
Businesses save on expenses on:
- Content production
- Prototyping
- Repetitive tasks
Democratization of Creation
With generative AI, non-experts can create:
- Visuals
- Written content
- Technical drafts
Limitations and Challenges of Generative AI
Despite its strength, generative artificial intelligence has actual drawbacks.
Hallucinations and Accuracy Issues
AI can generate assured but wrong results. This is an established danger of most generative AI models.
Bias in Training Data
In case of bias in the training data, the outputs can be affected or exaggerated.
Ethical and Copyright Challenges
Questions remain around:
- Content ownership
- Training data rights
- Attribution
Over-Reliance Risks
Overdependence on generative AI can decrease:
- Critical thinking
- Original creativity
- Human judgment
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Use
Careful use of generative artificial intelligence must be supported with careful protection.
Transparency
Users are supposed to be aware of AI-generated content.
Content Authenticity
Human review must be accurate and contextual.
Data Privacy
The use of sensitive or private data ought not to be carelessly done in generative AI systems.
Human Oversight
AI is best utilized as an assistant but not an authority.
Generative AI in Business and Everyday Life
How Companies Are Adopting It
Generative artificial intelligence is being implemented in organizations in:
- Marketing tools
- Customer support systems
- Internal workflows
Productivity vs Replacement Debate
Although job displacement is a concern, in most real use cases, the collaboration between humans and AI does not imply replacement, but it is a case of collaboration.
Collaboration Model
The most effective model combines:
- Human judgment
- Domain expertise
- Generative AI speed
Future of Generative AI
Where the Technology Is Heading
The future generative AI systems are likely to:
- Become more accurate
- Handle more modalities
- Blend well into appliances that we already have.
Regulation and Governance
Companies and governments are coming up with structures to guarantee:
- Ethical use
- Accountability
- Transparency
Skills Humans Will Still Need
Despite the development of generative AI, humans are required in:
- Strategy
- Ethics
- Creativity
- Decision-making
Conclusion
Generative AI is a significant structural change in the interactions between machines and content and creativity. Generative AI systems can use their experiences to produce text, images, audio, video, and code in a manner that becomes more and more natural by learning through large datasets and forecasting patterns.
Learning about generative AI and its functionality makes people and companies responsible and productive users of it. Generative AI is not as powerful as a substitute for human intelligence: it is a means of enhancing human capacity.
Implemented in a careful manner, generative AI can improve productivity, help in creativity, and create new possibilities in industries. The future is not in AI, but it is the human race that will know how to deal with it prudently.
Disclaimer: BFM Times acts as a source of information for knowledge purposes and does not claim to be a financial advisor. Kindly consult your financial advisor before investing.