Decentralized Finance is the Blockchain equivalent of traditional financial operations such as lending, borrowing, yield investing, currency swapping, and more. Since in DeFi, all these activities take place in a decentralized environment (i.e., on the Blockchain), it is called Decentralized Finance or DeFi.
Decentralized Finance started with the creation of Ethereum, which provided smart contract functionality. Smart Contracts are critical to creating a decentralized, automated, and trustless ecosystem in which human intermediaries are replaced by technology.
#Note: The short abbreviation for Decentralized Finance, i.e., DeFi, has been used a lot in this article.
History of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, began with the creation of Ethereum, which enabled blockchains to automate tasks. Automated processes for lending, borrowing, and staking enabled users to use the blockchain independently without any assistance. Further, since DeFi was fully transparent, with each action recorded in a decentralized ledger, there was no need for a central authority such as a bank.
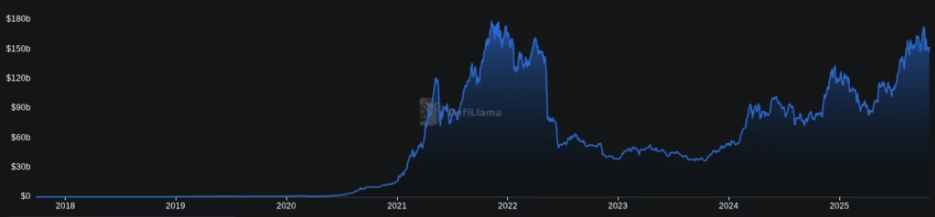
#Note: Total Value Locked (TVL) is the amount of crypto people have invested, deposited, lent, or collateralized on a chain. The data above is the total amount of all chains combined.
2015-18
Decentralized Finance, as a set of processes, began with the creation of Ethereum, which enabled users to stake, lend, borrow, swap, and bridge tokens without a central authority.
The initial DeFi actions were just limited to staking and then expanded into lending and borrowing as more people adopted blockchain technology.
2018-22
The little bear market of 2019 and the bull run till mid-2022 were the most significant growth phases for Decentralized Finance as it went mainstream in those periods. Staking was increasingly offered by more exchanges, with new Decentralized Exchanges popping up for users who needed anonymity.
The market peak reached in late 2021 and early 2022 was never matched in the next 4 years until 2025. The reason Decentralized Finance markets peaked in 2021 was excess liquidity. Subsequently, when Central Banks drained liquidity to prevent hyperinflation, the rally fizzled out.
2022-24
The bear market that started from March 2022 and ended in October 2024 left a big impact on DeFi markets, essentially wiping out a large chunk of capital
2024-Present
The next growth phase in Decentralized Finance started in November 2024 when Donald Trump won the US Presidential Elections. Hailed as a pro-crypto president, he nullified several anti-DeFi rules, such as the infamous DeFi Broker Rule.
However, over the last three months of 2024 and the full year of 2025, DeFi growth remained limited due to liquidity constraints in the US and European Economies, among others. This liquidity shortage was caused by high inflation, which was indeed the result of post-COVID stimulus packages.
Principles of Decentralized Finance
1. Decentralized Control
The basis of decentralized finance is that no single authority controls it. There is no central decision-making body, no central point of control, no single infrastructure. All controls are decentralized, i.e., decision-making is handled via DAOs and community voting. Further, the network that runs DeFi protocols is also decentralized, i.e., it is powered by hundreds of computers spread across a wide geographic area.
2. Distributed Ledger
Distributed Ledger refers to the distributed nature of Blockchain, which means everyone has equal access to all the transaction data (anonymized) without any bias. Every transaction is updated in real time across the network, which is simultaneously run by thousands or millions of computers worldwide.
3. Permissionless
You should not require any permission, nor any KYC or verification, to be a part of any true Decentralized Finance network. All you need is cryptocurrency and a wallet, and you can perform all kinds of transactions supported by the network.
4. Anonymity
Anonymity is at the core of Decentralized Finance. All transactions in blockchain technology are anonymized, meaning they do not contain any direct information about the sender or receiver. Further, since every transaction and wallet address is public, they do not ask for any KYC or personal identification to create accounts.
However, centralized exchanges may require KYC for legal compliance.
5. Self-Custody
Self-custody is the concept of keeping your wallet keys with you to get 100% ownership of your cryptocurrencies.
The concept took the world by storm when, in 2022, the FTX exchange collapsed, taking billions worth of investor funds with it. Exchanges usually keep your wallet keys with them and provide you with a password function to log in and recover your account.
However, in the world of crypto, full control is with the person who has the keys.
As a result, self-custody is considered vital in DeFi and Blockchain.
Types of DeFi Activities
Lending
You can lend any cryptocurrency (that supports DeFi) to anonymous borrowers for some interest and collateral. If they default on payments, the collateral is for you to keep.
Borrowing
Borrowing in crypto takes place via DeFi protocols, where you can get a crypto loan by pledging some collateral, such as NFTs, liquidity tokens, etc.
Staking
Staking is the act of locking your crypto on a staking platform, typically to earn lending or governance rewards. It is the oldest way of earning a passive income in Decentralized Finance.
Ethereum was the oldest cryptocurrency that could be staked and still has the largest market share.
Yield Farming
Yield Farming is the act of moving your funds from one liquidity pool to another to maximize the rewards. If one pool offers more rewards, yield farmers move their funds to that pool and keep doing it.
It is often done in an automated way via bots, smart contracts, smart wallets or AI Agents.
Liquidity Providing
Liquidity Providing is the concept of depositing your tokens into a liquidity pool in order to get rewards. These rewards could be in the form of discounted Liquidity Provider(LP) tokens or rewards.
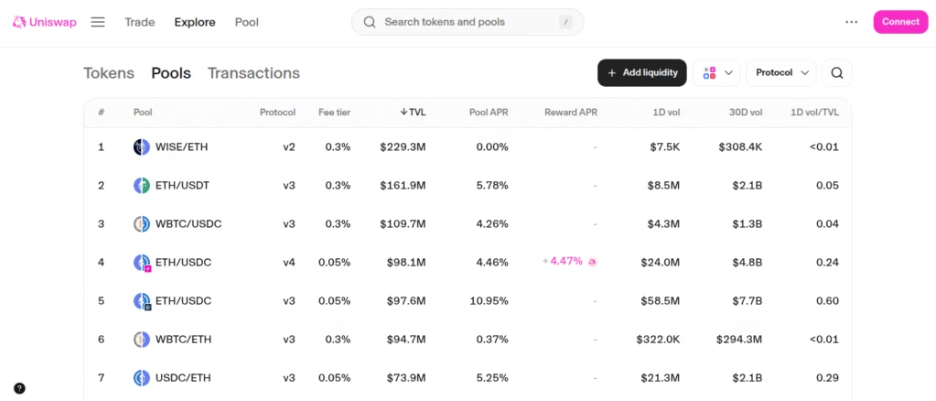
When you deposit any crypto, such as Ethereum or Stablecoins, to a liquidity pool, you get LP tokens, which you can again stake at re-staking protocols, giving you double rewards.
Swapping
Swapping is the action of changing one coin to another on the same blockchain.
For example, you can swap ETH for USDT or vice versa on UniSwap.
Swapping on Uniswap, a multi-chain DeFi Protocol
Bridging
Bridging is the act of moving a cryptocurrency from one chain to another. This helps the user unlock different benefits provided by different chains.
For example, you can bridge your ETH, USDT, UNI, or any token from Arbitrum/Optimism/Linea/Polygon to Ethereum for better safety, or you can do the reverse for lower transaction fees.
In-App Bridging Protocol of MetaMask, a DeFi-enabled Wallet
Disclaimer: BFM Times acts as a source of information for knowledge purposes and does not claim to be a financial advisor. Kindly consult your financial advisor before investing.













